Dementia continues to pose a significant challenge in neuroscience and clinical care, affecting millions worldwide. Early detection is pivotal in slowing disease progression and implementing preventive interventions. Life sciences are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance early detection, enabling researchers and clinicians to identify dementia years before clinical symptoms appear.
AI in Neuroimaging and Biomarker Analysis
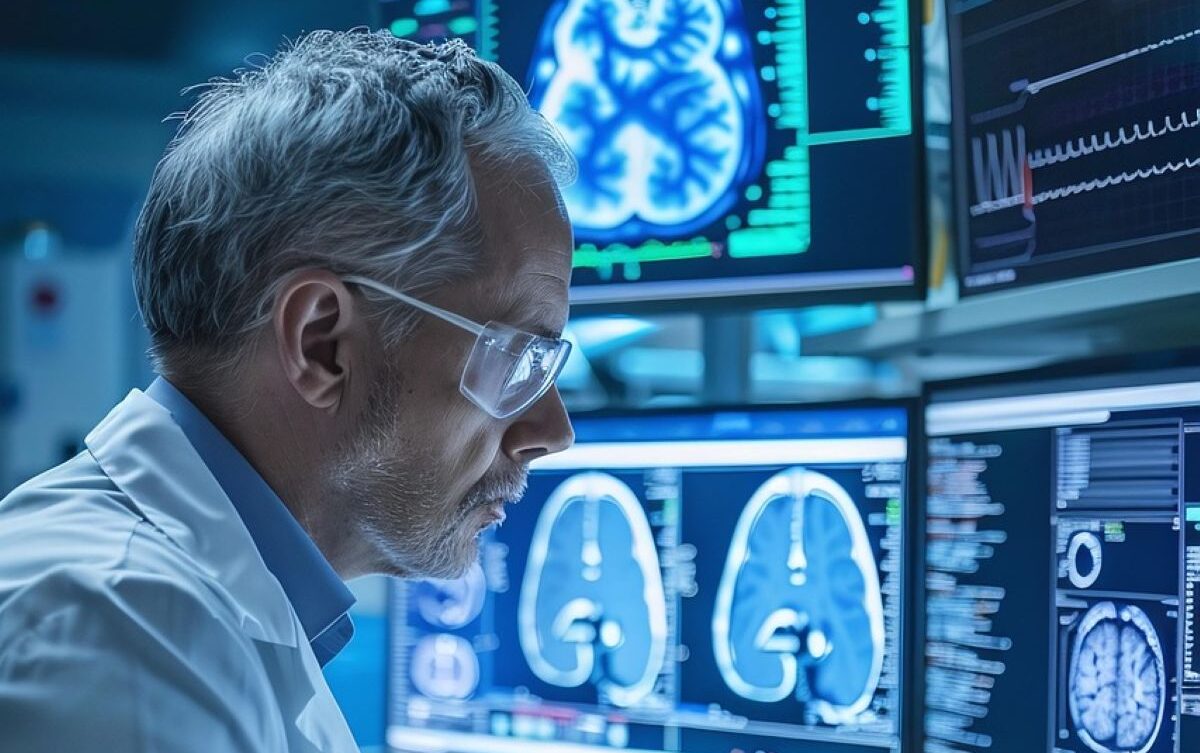
One of the most promising applications of AI in dementia research lies in neuroimaging. Advanced machine learning algorithms can process large volumes of brain imaging data, including MRI and PET scans, to identify subtle structural and functional changes that precede clinical onset. AI-driven analysis of hippocampal atrophy, cortical thinning, and amyloid deposition can detect early pathological signatures of Alzheimer’s disease. By integrating neuroimaging data with patient demographics and clinical histories, these algorithms provide a more precise and predictive assessment of dementia risk than conventional methods.
In addition to imaging, AI models are increasingly being applied to biomarker analysis. Blood- and cerebrospinal fluid-based biomarkers, such as amyloid-beta, tau proteins, and neurofilament light chain, offer quantifiable indicators of neurodegeneration. Machine learning approaches can combine these biomarker profiles with longitudinal clinical data to forecast disease progression, enabling early therapeutic interventions and personalised care strategies.
Predictive Modelling and Multi-Omics Integration
AI in life sciences is also facilitating predictive modelling through multi-omics integration. Genomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and transcriptomic data provide a holistic view of the molecular pathways involved in dementia. Sophisticated AI models can detect intricate patterns across these datasets, uncovering new risk factors and early disease markers that traditional statistical methods might overlook. By identifying high-risk individuals before cognitive decline manifests, these tools allow targeted lifestyle interventions, clinical monitoring, and inclusion in preventative clinical trials.
Clinical Applications and Early Intervention
Early detection powered by AI is not merely a research milestone; it has direct clinical implications. In practice, AI-supported diagnostic tools can flag at-risk patients in primary care, enabling neurologists to implement cognitive assessments and therapeutic plans sooner. For example, some AI systems can analyse subtle speech or handwriting changes, behavioural patterns, or digital biomarkers from wearable devices to detect early cognitive impairment. These non-invasive methods complement traditional diagnostic techniques, offering a multi-layered approach to dementia detection. AI technologies are already being applied in patient care, supporting caregivers and clinicians alike.
Dr. Sarah Tabrizi, a neuroscientist at University College London, emphasises:
“Integrating AI with molecular and imaging biomarkers transforms our ability to identify Alzheimer’s disease before patients experience noticeable symptoms, opening a critical window for preventative strategies.”
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI shows tremendous promise in life sciences, its integration into early dementia detection raises scientific and ethical challenges. Data privacy, algorithmic bias, and reproducibility of predictive models remain key concerns. Ethical considerations, including patient consent and transparency of AI decision-making, must be rigorously addressed to ensure clinical utility and trustworthiness.
Future Directions in Life Sciences Research
The convergence of AI and life sciences is set to redefine dementia research and care. Ongoing studies aim to refine AI algorithms for earlier, more accurate detection, integrating neuroimaging, biomarker profiling, and multi-omics datasets. Advances in AI technologies hold the potential to transform understanding, diagnosis, and care strategies. As these technologies mature, AI may become an indispensable tool in personalised preventative strategies, clinical trial design, and neurodegenerative disease research.
Harnessing AI for early detection of dementia exemplifies the transformative potential of computational life sciences, bridging molecular insights, clinical application, and technological innovation to improve patient outcomes.