The life sciences landscape in northern England is undergoing a dynamic evolution, driven by the growing importance of advanced therapies such as cell and gene treatments. These innovative approaches, which aim to treat or cure diseases by intervening at the level of cells or genes, are now being supported by new infrastructure, workforce development and regional strategy focused not just on London and the South East but across the north of England.
Why northern England?
Several factors make the north of England a strong candidate for advanced therapy hubs:
- Regional government and industry policy emphasising levelling up to spread life science investment beyond the traditional clusters
- Established research strength in key universities and NHS institutions in the north
- The need for manufacturing, clinical translation and workforce training infrastructure to support advanced therapies. For example, the Northern Alliance Advanced Therapies Treatment Centre covers populations across North East England and Scotland and is focused on delivering advanced therapy clinical infrastructure
- Growing interest among investors and government in biomanufacturing and advanced therapy pipelines across the UK, including northern locations, as highlighted by Oxford Global
Key hubs and developments
Here are some of the standout developments in cell and gene therapy infrastructure in northern England:
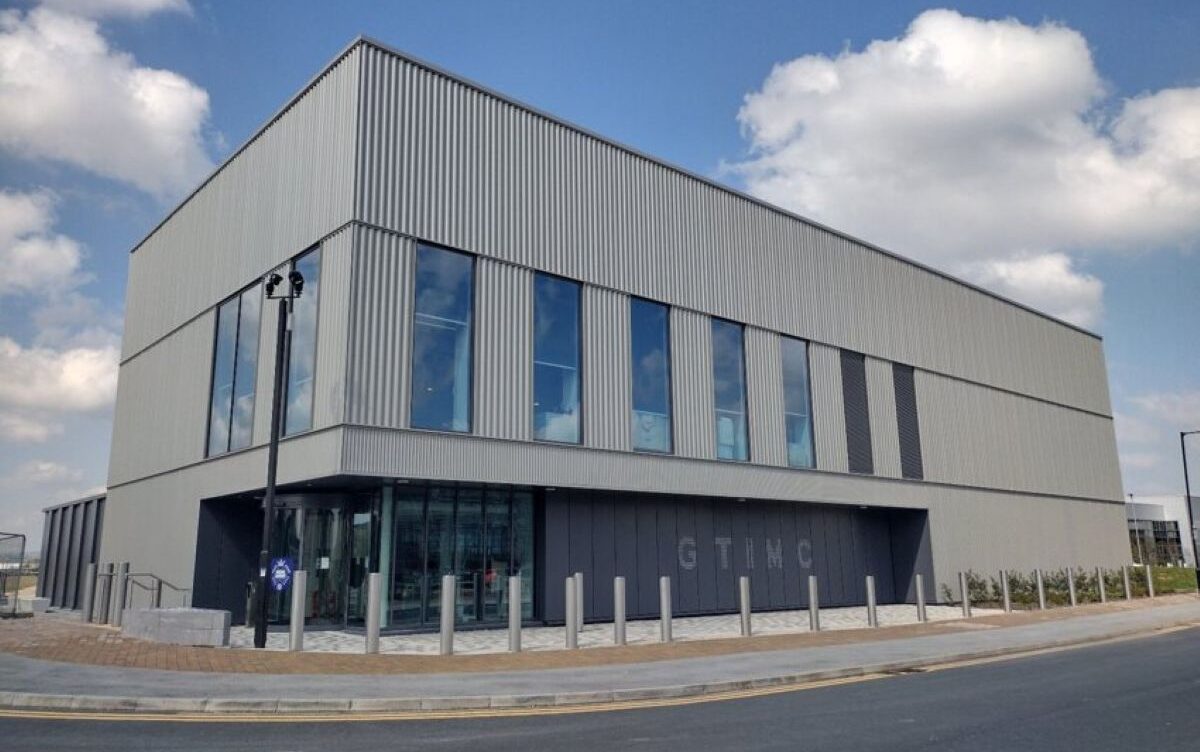
University of Sheffield – Gene Therapy Innovation and Manufacturing Centre (GTIMC)
The University of Sheffield has established a dedicated centre for gene therapy innovation and manufacturing. It is designed to accelerate the translation of gene therapies into clinical trials for conditions including motor neurone disease, cystic fibrosis and haemophilia.
Key points:
- The centre provides clinical grade manufacturing and translational support, backed by LifeArc
- Locating this facility in Sheffield signals a deliberate choice to develop capacity outside the traditional life science hubs of London and the south
- It positions Sheffield as a major player in the UK’s advanced therapy ecosystem
Manchester and the North West region – Advanced Cell and Gene Therapy Efforts
In the North West, Manchester is emerging as a hub for advanced cell and gene therapy research and development. The region has been at the forefront of research into advanced therapies for cancer and other diseases.
Highlights:
- The region benefits from established research institutions and clinical networks
- There is a focus on aligning levelling up policy with life sciences investment
- The challenge remains to build full manufacturing and supply chain capacity to support these therapies at scale
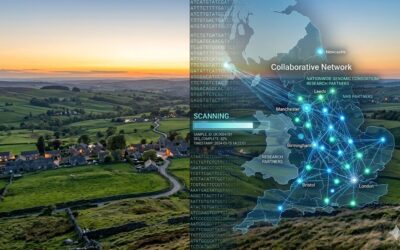
Northern Alliance Advanced Therapies Treatment Centre – North East England and Scotland
The Northern Alliance Advanced Therapies Treatment Centre (NA-ATTC) covers North East England and Scotland and is focused on building infrastructure, training and clinical delivery pathways for advanced therapies under the NHS.
Key aspects:
- The reach is approximately 15 million people across two health systems
- Focus on workforce upskilling in advanced therapy medicinal products and best practice delivery
- Serves as a foundation for bringing therapies from the lab to the patient in the region
What this means for the ecosystem
The emergence of these hubs in northern England creates several important implications for the life sciences ecosystem:
- Manufacturing capacity: advanced therapies often require highly specialist manufacturing such as viral vectors and cellular processing. Having regional hubs means therapies can be developed and manufactured closer to patients and researchers, reducing logistical complexity
- Clinical trial access and translation: with local hubs, the translation from research to clinical trial becomes more feasible, allowing northern England to capture more of the value chain rather than simply being a site for later phase trial recruitment
- Workforce development: the advanced therapy field is highly specialist. Training and workforce development are key, and regional hubs can build local talent rather than relying exclusively on centres in the south
- Economic growth and regional regeneration: the life sciences sector offers jobs, investment and high value added growth. Locating hubs in northern regions aligns with levelling up aims
- Patient benefit: the presence of these hubs increases the likelihood that patients in the north of England will benefit from cutting edge therapies sooner
Challenges and next steps
Though momentum is strong, a number of challenges remain:
- Cost and scale: cell and gene therapies tend to be expensive and complex, and scaling manufacturing remains a barrier. The Manchester commentary raised the issue that these therapies challenge cost effectiveness calculations as they are very expensive when assessed by payers
- Supply chain and equipment constraints: the UK has faced challenges in importing specialist equipment post Brexit, which can hinder manufacturing readiness, as reported by Oxford Global
- Regulatory and commercial translation: ensuring that regional hubs are integrated into broader commercial and regulatory pathways is essential
- Infrastructure investment: while the hubs exist, many will need further investment to reach full capacity, including vector manufacturing, analytics and quality assurance
- Collaboration across the UK: ensuring northern hubs are well connected to national networks, industry partners and global supply chains will be critical
Northern England is rapidly becoming a major player in the advanced therapy space. With centres such as Sheffield’s Gene Therapy Innovation and Manufacturing Centre, Manchester’s life sciences efforts and the Northern Alliance Advanced Therapies Treatment Centre, the region is building the infrastructure, talent and clinical pathways needed for cell and gene therapies to flourish.
For companies, researchers and policy makers, this offers a compelling proposition: a growing ecosystem outside traditional southern hubs, with the potential for patient benefit, regional economic growth and life sciences leadership. The coming years will reveal how these hubs translate their potential into therapies delivered at scale, but the foundations are now clearly in place.